- Swiss testing laboratory
BS EN 13697

Hassle-free testing experience
Need to get a product tested? No worries! To and fro logistics are on us; we collect your products, test them and, deliver them back to you.
Related tests for you
Quick understanding of the test
EN 13697:2015+A1:2019 - Quantitative non-porous surface test for the evaluation of bactericidal and/or fungicidal activity of chemical disinfectants used in food, industrial, domestic and institutional areas
- Bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus hirae
- Fungi/Yeast: Aspergillus brasiliensis, Candida albicans
- A stainless steel surface is used as a carrier for the test.
- Test strains are inoculated onto the carrier and allowed to dry.
- Disinfectant is applied to the dried microbial film on the carrier surface.
- After the contact time, the dried inoculated surface is neutralized, and the surviving microorganisms are quantified.
- This standard closely mimics practical usage conditions, ensuring the test results are highly relevant to real-life applications.
- It covers a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi.
Turnaround Time
- ≥ 4 log reduction for bactericidal activity.
- ≥ 3 log reduction for fungicidal/yeasticidal activity.
Do you have a product that needs testing?
Abstract
BS EN 13697 is the European standard test method for assessing the bactericidal and fungicidal activity of chemical disinfectants intended for use on non-porous surfaces. This method ensures that the disinfectants used in food preparation environments, hospitals, and public facilities can efficiently kill bacteria, yeasts or molds that can pose serious health risks if left untreated.
This test method simulates practical conditions under which disinfectants are used on non-porous surfaces with or without mechanical action like scrubbing or wiping. The method tests disinfectants both under clean and dirty conditions thus providing an all-round analysis of whether disinfectant agents significantly decrease microbial contamination during practical usage.
EN 13697 test conditions & requirements
- Test temperature – In the range of 4 °C and 40 °C. For tests carried out at room temperature, the temperature may range from 18 °C to 25 °C
- Contact time – As per manufacturer’s instructions, typically ranging from 1 min to 60 mins.
- Mandatory test organisms – Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538P), Aspergillus brasiliensis (ATCC 16404), Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 15442), Enterococcus hirae (ATCC 10541), MRSA (ATCC 33591), Salmonella enterica (ATCC 10708), Candida albicans (MTCC 3017)
- Interfering substance – It is required to check the efficacy of the test samples under both dirty and clean conditions to simulate conditions that coexist with microbes in natural environments.
Products tested using EN 13697 test method at MIS
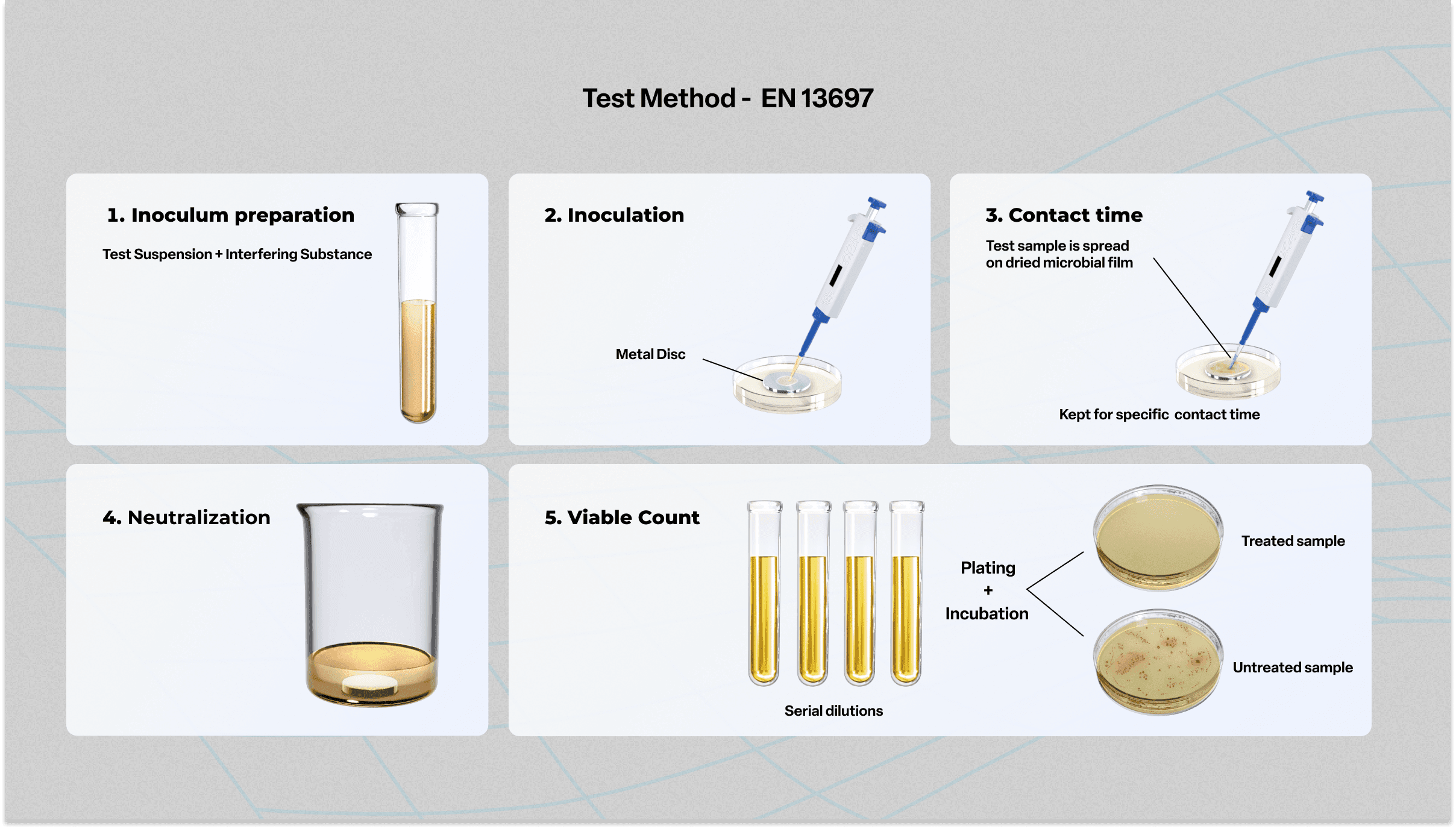
EN 13697 test method
- A test suspension containing the target organisms is added to an interfering substance.
- The mixture is then inoculated onto a non-porous surface like glass or stainless steel and is allowed to dry.
- The test product (sample) and the control (hard water) are then applied to the surface containing the dried microbial film.
- The surface is maintained at the specified temperature for a defined contact time as instructed by the manufacturer.
- After the contact time lapses, the surface is neutralized using a neutralizing solution to halt the disinfectant action.
- The surviving microorganisms are then quantified to assess the efficacy of the disinfectant.
- The difference between the initial microbial count and the surviving count after disinfectant treatment is calculated as the log reduction value.
Factors affecting EN 13697 test method
- Concentration of disinfectant: The strength of the disinfectant solution can affect its ability to eliminate microorganisms. Manufacturers instructions must be carefully followed to ensure accuracy in results.
- Contact time: Contact time depends on the concentration of the formula. The test is usually conducted following the contact time provided by the manufacturer.
- Temperature: Higher or lower temperatures may impact the disinfectant’s activity.
- Interfering substances: The presence of organic materials such as dirt or food residues can reduce the efficacy of the disinfectant.
Importance of BS EN 13697 standard test
Regulatory and compliance for EN 13697 testing
Advantages of the test method
The advantages of performing this test method are
- It closely mimics the conditions found in everyday usage thus providing reliable results.
- The method applies to disinfectants used in a wide range of environments, including food processing, industrial cleaning, and household use.
- By testing under both clean and dirty conditions, the standard ensures that disinfectants are effective in various scenarios.
- It tests both bactericidal and fungicidal activity of disinfectants, thus encompassing a very wide range of microorganisms.
At Microbe Investigations Switzerland (MIS), we specialize in conducting EN 13697 tests to validate your disinfectant products. Our experienced team provides comprehensive testing services to ensure your products meet the required bactericidal and fungicidal standards.
For antimicrobial efficacy of surface disinfectants, MIS also performs EN 1276 and EN 14476 test methods.
For more information on our test pricing, facilities, and services, contact our team experts today.
Frequently Asked Questions

DR. Martinoz Scholtz
At Microbe Investigations Switzerland, we perform the tests using Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 15442), Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538P), Enterococcus hirae (ATCC 10541), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 4352), MRSA (ATCC 33591), Salmonella enterica ( ATCC 10708), Candida albicans (MTCC 3017). Additional strains can be added on request.
EN 1276 is a suspension test, while EN 13697 is a surface test used to assess the disinfectant efficacy.
Meet the best of the blend of
R&D, Efficacy Testing,
Innovation and Passionate
Experts at MIS.





Explore More
Fungicidal disinfectant testing plays an
Antimicrobial testing is important to
Antibacterial efficacy testing is an
Biocidal products regulation Biocidal products






