Understanding the dynamics between the bacterial pathogens and the drugs meant to interfere with their growth processes is of great importance in the development and optimization of antibiotic treatments. One of the most critical measures within this process is Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC). The article discusses the need for MIC test for antibiotic potency, the methodologies used in such tests, the implications on antibiotic resistance, and the future of antibiotic development.
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Definition and Importance
Minimum inhibitory concentration is defined as the lowest concentration of an antibacterial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism following an overnight incubation. The MIC values play an important role in predicting the efficacy of antibiotic compounds and in guiding recommendations of dose when they are put to use in treatment. Proper determination of MIC gives a chance to caregivers to use antibiotics strategically and optimize the therapeutic outcome with minimal development of antibiotic resistance.
Methodologies in MIC Testing
- Broth Dilution Method
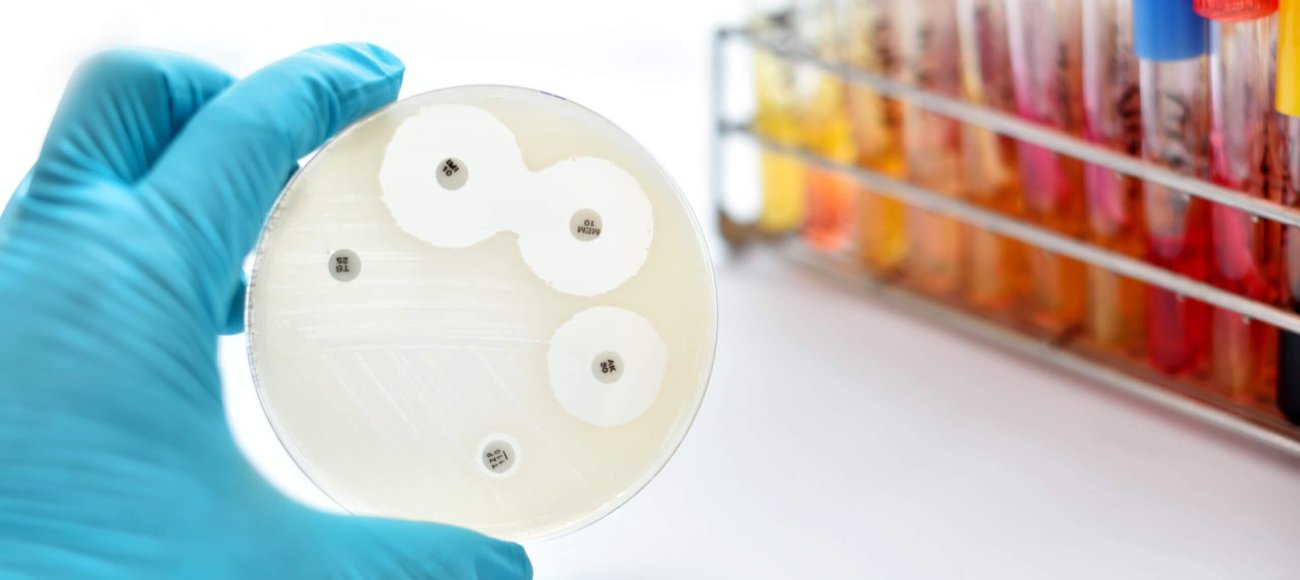
The broth dilution method used to define MIC is most frequently performed in tubes or in microtiter plates. Here, the antibiotic is subjected to serial dilution in the broth followed by addition of a standard number of bacteria in each dilution. After incubation, the lowest antibiotic concentration that inhibits visible growth is recorded as the MIC. - Agar Dilution Method
The agar dilution method consists of the serial dilution of antibiotics in agar plates, which are later spot-inoculated with bacteria. Following incubation, the growth pattern is visually inspected for MIC determination. - E-test
E-test is a commercially available strip which combines features of both the diffusion and dilution techniques to determine MIC. A strip is impregnated with a gradient of antibiotic concentration and then placed on an agar plate that has been inoculated with the organism. The MIC is read where the elliptical zone of inhibition intersects with the strip, and it provides a very easy and accurate way to determine MIC.
MIC and Antibiotic Resistance
- Role in Resistance Management
Precise MIC testing has important implications in the management of antibiotic resistance. Being able to define the threshold of antibiotic effectiveness in very precise terms allows clinicians to avoid possible under-dosing which could induce subtherapeutic exposure and the development of resistance, or overdosing, known to bring about other adverse effects of medication. - Surveillance and Adjustments
Regular monitoring with MIC testing provides for the surveillance of resistance trends over time. Such data are invaluable when creating the guidelines for treatment updates and for informing practices in clinical settings. This will also help in designing new antibiotics or modifying the current ones in a manner that pharmaceutical companies can produce antibacterial drugs that can effectively fight against resistant strains.
Future Perspectives in MIC Testing
- Advancements in Technology
MIC testing is likely to change dramatically with emergent technologies. Innovations such as automated systems, digital imaging, and AI-driven predictive modeling are likely to make determinations of MIC significantly faster and more accurate. This would allow for a much more personalized therapy with antibiotics and modulation of the therapy according to the MIC data from the individual. - Integrating MIC Data with Genomic Information
MIC testing in combination with genomic data can give better insight into bacterial resistance mechanisms. Such integrative approaches are likely to help in the design of targeted antibiotics that are more effective toward particular bacterial strains showing pathways linked with resistance. - Challenges and Solutions
Despite the rapid progress of technology, the costs of such tests, accessibility, and the need for standard interpretation are some of the challenges that remain. This, taken together with international collaboration and policy-making, will be necessary in order to harness the full potential of MIC testing.
Role of MIS
At Microbe Investigations Switzerland, we provide comprehensive Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) testing to help you fine-tune the potency of your antibiotics. Our expert microbiologists use state-of-the-art methodologies to deliver precise and reliable results, ensuring your antibiotics are both effective and safe. Trust MIS to support your antibiotic development with accurate MIC testing tailored to meet the highest industry standards.
To explore how our MIC testing services can enhance your antibiotic formulations, or to schedule a consultation, please contact our knowledgeable experts today.